To understand the strategies that states undertake to expand coverage and initiate broader health reform, it is important to recognize the variability in states’ health coverage distribution, employer-sponsored insurance rates, and public program eligibility levels. The charts below highlight certain aspects of Oklahoma's coverage landscape. The graphs also provide a comparison to national data to give a sense of how Oklahoma is faring.
For more information on specific coverage programs implemented in this state, please click on the ‘Coverage Strategies’ tab.
Overview of Medicaid and SCHIP Coverage[1]
Group | Income Eligibility |
Children | 185% FPL (ages 0-19) |
Pregnant Women | 185% FPL |
Parents | 36% FPL |
Adults[2] | 200% FPL |
SSI Disabled (non-elderly) | 74% FPL |
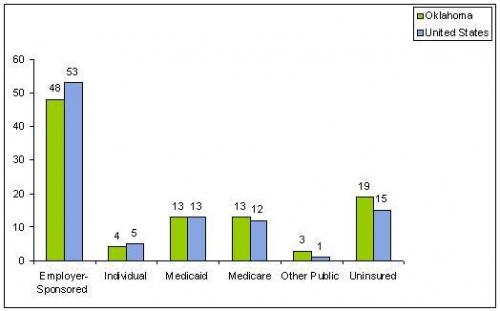
Sources of Health Insurance Coverage State Data 2006 – 2007, U.S.[3]
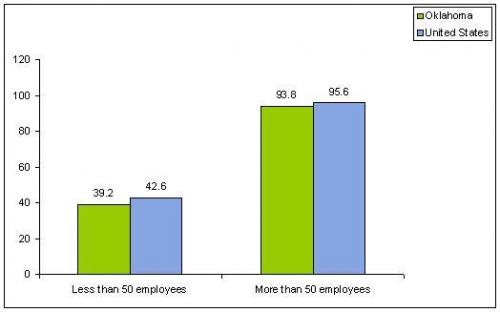
Percentage of Private-Sector Establishments That Offer Health Insurance Based on Firm Size by State, 2006[4]